- Before we dive deep into Computer Networks lets understand some basic stuffs and terminologies
What is a network?
- Computers that are connected together
What is Internet?
- The collection of these computer networks
Protocols:
- These are just rules that are defined by the internet society
TCP:
- It ensures that the data will reach its destination and it will not be corrupted on the way.
UDP:
- There would be chances of data corruptibility when we use this protocol.
HTTP:
- This is used by the web browser.
- It defines the format of the data that is being transferred between web clients and servers
- Note: every single device that talks to each other over the internet have an IP address
- NAT:
- After getting a response from the internet, now the modem will decide which device initially sent the request -- this is done using NAT.
- Note:
- IP address : decides to which device to send the data
- Ports : decides to which application to send the data in that device
- Ports are 16-bit number
- Tota port nos. possible->2^16
Good To Know Stuff:
- All the HTTP stuff will happen on port 80.
- Reserved ports--> 0-1023
- Registered for applications(e.g. MySQL,mongoDb)--> 1024-49152
Some Terminologies:
LAN:
- If we have some devices connected in a small house/office then its known as LAN
- e.g.- Ethernet cable, WIFI
- If we have some devices connected in a small house/office then its known as LAN
MAN:
- If the connection is across a city
WAN:
- If Connection is countries
- e.g.- Optical fibre cable
- If Connection is countries
SONET:(Synchronous Optical Network)
- It carries the data using optical fibre cable, hence it can cover larger distances
Frame Relay:
- It is a way for you to connect LAN to the internet
What is Modem?
- It is used to convert the digital signal into analogue signal and vice-versa
What is Router?
- It is a device that routes the data packets based on their IP Addresses.
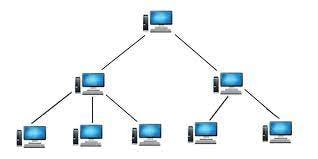
Topologies:
Bus:
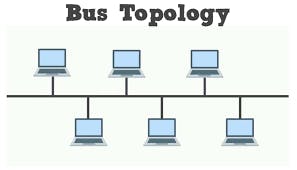
- Disadvantages:-
- If the central wire gets broken,entire system is spoiled
- Only one person can send data at one particular time.(Through central wire)
Ring:
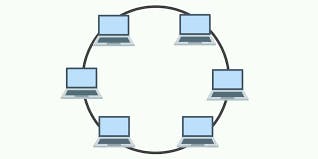
- Every system communicates with one another
- Disadvantages:-
- If one of the cables break,then its spoiled
- Lot of unnecessary calls are being made
Star:
- Disadvantages:-
- If Central device fails then system is spoiled
Tree:(Bus+star)
Mesh:
- Every single component connected to every single component
- Disadvantages:-
- Expensive
- Scalability issues
- Now as we are clear with the basic stuff let's dive deep into computer networks*
Structure Of Network:
OSI Model:(Open System Interconnection Model)
- 7 layers of OSI model:
- Application layer
- Presentation layer
- Session layer
- Transport layer
- Network layer
- Data link layer
- Physical layer
APPLICATION LAYER:
- Human-computer interaction layer
PRESENTATION LAYER:
- The presentation layer will convert the data into machine representable binary format -- This process is known as translation
- This layer also provides abstraction.
SESSION LAYER:
- This layer helps in setting up and managing the connections and it enables the sending and receiving of data followed by termination of connected sessions.
TRANSPORT LAYER:
- This layer works with data and makes sure it is transported easily.
- It does it in 3 ways:
- Segmention: The data which is received from session layer will be divided into small data units called Segments.
- Segments <- Every segment will contain the source and the destination's port no. and a sequence no.
- sequence no. helps to reassemble the segments in correct order
- Segments <- Every segment will contain the source and the destination's port no. and a sequence no.
- Flow control: It controls the amount of data that's being transported
- Error control: It adds something known as "checksum" to every data segment,that way it can figure out whether data that was received was good or bad
- Segmention: The data which is received from session layer will be divided into small data units called Segments.
NETWORK LAYER:
- This layer basically works for the transmission of received data segments one from computer to another that is located in different networks.
- e.g. Routers
- Function of network layer:
- Logical addressing:
- Network layers assign the sender's and receiver's IP addresses to every segment and it forms an IP pocket. So that every data packet can reach the correct destination.
- Logical addressing:
- This layer basically works for the transmission of received data segments one from computer to another that is located in different networks.
DATA LINK LAYER:
- This layer allows you to directly communicate with the computers.
- Data Link layer will receive the data packet from the network layer and this data packet contains the IP addresses of both sender and receiver
- Note:
- Logical addressing: This is done at the network layer which is IP addresses and stuff.
- MAC addressing: This is physical addressing, the address of sender and receiver are assigned to the data packet to form a frame
- Frame: It is a data unit of the data link layer.
- Remember: MAC address is a 12 digit alpha-numeric no. of the network interface of the computer( MAC-> Media Access Control)
PHYSICAL LAYER:
- This is the hardware part
- In this layer you work with cables and stuff
- This layer will convert the data into electrical/optical signal
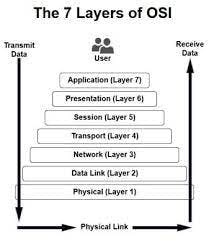
- 7 layers of OSI model:
TCP/IP Model: (Practically used model)
- It is known as Internet Protocol Suit
- 5 layers of TCP/IP Model:
- Application layer
- Transport layer
- Network layer
- Data link layer
- Physical layer
- Deep Dive on TCP/IP Model
APPLICATION LAYER :
- It is the main layer where the user interacts, it consists of applications
- e.g. Whatsapp, browser etc.
- It is present in individual devices.
- Client-Server Architecture
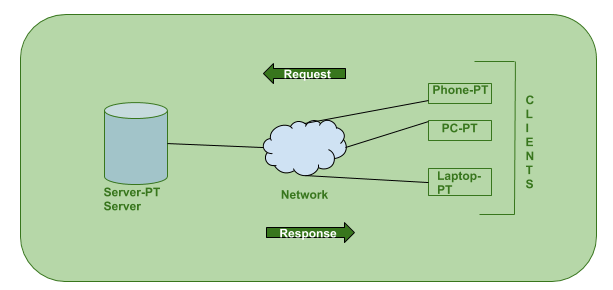
- What is a server?
- It is a system that controls the website you are hosting.
- Data centres:
- Collection of many servers at a place
- They may have static IP addresses
- High upload speed
- What is a ping?
- It measures the round trip time for messages sent from the originating host to destination
- P2P architecture
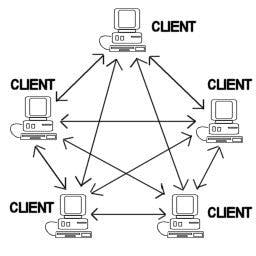
- Various devices get connected with each other
- There is no one server present
- Each computer acts both as server and client
- e.g. Bit torrent
- SOME TERMINOLOGIES:
- Repeater-
- Operates at the physical layer
- Its job is to regenerate the signal over same network before it becomes too weak or corrupted
- Its a two port device
- Hub-
- It is a multiple port repeater
- It connects multiple wires from different branches
- It regenerates the network
- Bridge-
- Operates at the data link layer
- Bridge is a type of repeater
- It has an additional functionality -- It can filter out the content by reading MAC address of source and destination
- Switch-
- It is a multi port bridge that can boost the performance and efficiency
- It can perform error checking before forwarding the data,so it makes it very efficient
- Gateway-
- It's a passage to connect two networks together that may work upon different networking models
- Repeater-
- Some Gyaan On Protocols:
- HTTP:(Hyper-Text Transfer Protocol)
- This is used by the web browser.
- It defines the format of the data that is being transferred between web clients and servers
- DHCP:(Dynamic Host Control Protocol)
- It allocates IP address to the devices connected to the network
- FTP:(File Transfer Protocol)
- Files are transferred using this protocol
- Note: It is not used these days anymore
- Files are transferred using this protocol
- SMTP:(Simple Mail Transfer Protocol)
- It is used to send emails
- IMAP & POP3:
- These are used to receive emails
- SSH:
- If you want to login to a terminal of someone else's computer then use SSH
- VNC:(Virtual Network Computing)
- Its used for graphical controlling
- Telnet:
- It is basically a terminal emulation that enables the user to connect to a remote host/device using a telnet client
- UDP:
- Stateless Connection
- Data may be lost
- This protocol is used in video calling
- HTTP:(Hyper-Text Transfer Protocol)
- Program:
- Program is just like an app
- For e.g. Flipkart,amazon etc
- Process:
- One of the features of the program
- One program can have many many processes running at the same time
- Thread:
- It is lighter version of process.
- One process can have multiple running threads
- Remember: Thread is doing one single job
- Program is just like an app
- Sockets:
- When you need to send messages from one system to another system, use sockets for that
- Ports:
- Remember:
- IP address tells us which device we are working with.
- Ports tells us which application we are working with.
- Ephemeral ports:
- Let's say you have port 80 reserved for HTTP, so the application will internally assign itself random port no., when the process is done it will be freed.
- Ephemeral ports can exist on the client-side but on the server-side you have to know the port no. .
- Remember:
- HTTP:
- It's a client-server protocol and it tells us how the server will send back the data to the client
- It's a stateless protocol which means that the server will not store any information about the client by default
- HTTP uses TCP protocol
- TCP makes sure that all the data is received and everything
- HTTP Methods:
- Methods tells the server what to do and all
- GET: You are requesting some data
- (Give me this webpage, this youtube video etc)*
- GET: You are requesting some data
- POST: I am a client and I am giving something to the server
- (e.g.-> Webform i.e Username,password etc)*
- POST: I am a client and I am giving something to the server
- PUT: It put data at a specific location
- DELETE: If you want to delete data from the server. You will have to send a delete request
- STATUS CODES:
- 1XX -> Informational
- 2XX -> Success
- 3XX -> Redirecting
- 4XX -> Client error
- 5XX -> Server error
- Cookies:
- It is a unique string
- It is stored on the client's browser
- When you visit a website for the first time--> it will set a cookie and after that whenever you make a new request, in that request's header cookies will be sent.The server will know this request is coming from Amaan's computer
- Remember: Cookies have an expiration date
- Third Party Cookies:
- These are cookies that are set for the URLs that you do not visit
- Emails:
- How do Emails work?
- SMTP(Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) is used to send an email
- POP3 & IMAP are used to receive email
- Above protocols are application layer protocols
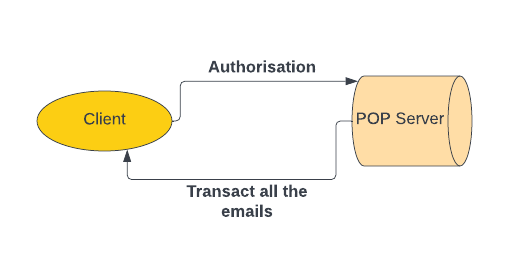
- POP:
- You first connect to the POP server (using TCP) , it does all the authorisation and stuffs and then you(client) asks the server for all emails
- IMAP : (Internet Message Access Protocol)
- it allows you to view your emails on multiple devices
- How do Emails work?
- DNS:(Domain Name System)
- We can say DNS is a directory
- We know that Domain Names are mapped to IP addresses and we use a service to look at these databases
- The most popular service for this is DNS
- Mechanism: When you enter "Google.com",it will use DNS to find the IP address of google's server
- So basically what happens is ->
- You type "Google.com" --> HTTP protocol will take that domain name & use DNS and it will convert the URL into the address --> then it will connect to the server.
- So basically what happens is ->
- Sub-domain : Second-level Domain : Top-level domain
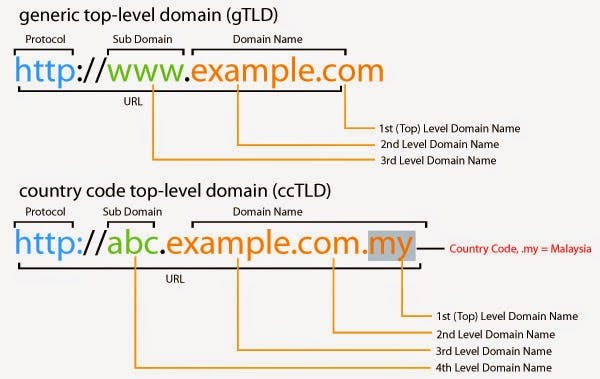
- So instead of storing everything in one database, there are multiple databases for these 3 categories
- It is the main layer where the user interacts, it consists of applications
TRANSPORTATION LAYER:
- Transport layer is the layer that lies inside the device
- Role of transport layer:
- It's to take the info (Whatever message your friend is sending) from the network to the application within the computer
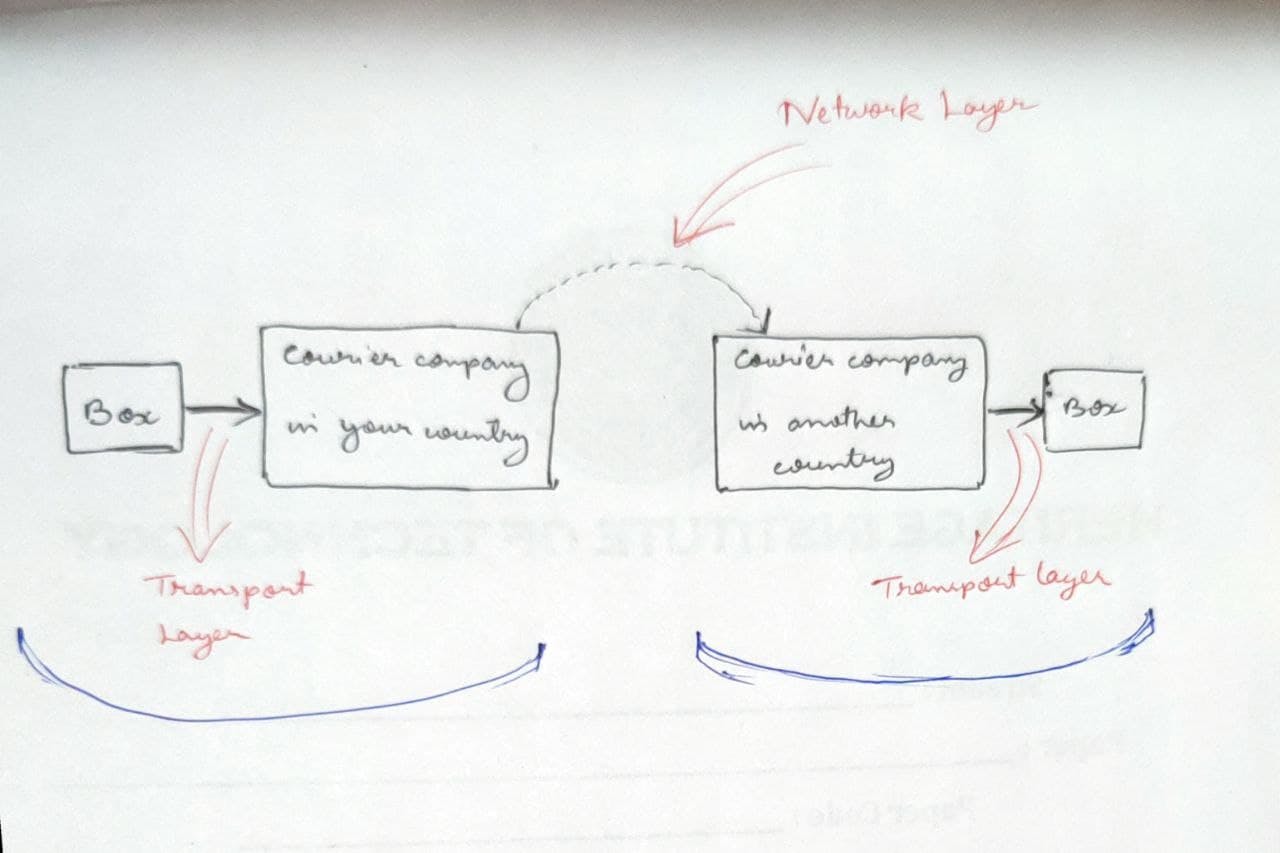
- Note: The transportation of info from one computer to another computer is done by the network layer
- Real Life Example of Network layer and Transport layer:
- Protocols in transport layer:
- TCP=> Data is not lost while using this protocol
- UDP=> Data can be lost in UDP
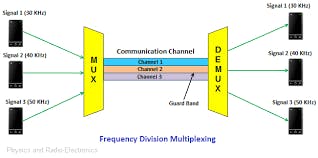
- Multiplexing & Demultiplxing
- Multiplexing allows us to send all the messages, files etc to a lot of destinations via just one medium
- Demultiplexing is the opposite of multiplexing
- Note: -
- Transport layer also takes care of congestion(traffic)
- Congestion control algorithms are built in the TCP protocol
- Note: -
- Checksums:
- Imagine it like some number
- You are sending data to your friend ---> Using that data you will calculate a value (i.e checksum) ---> Then your friend receives this modified data ---> Now the value of checksum is compared which was received and sent ==> Its the value is same then the data is not corrupted else it's corrupted
- Timers:
- If the data packets get lost during transmission, then timers help to know about it
- "you can google about timers to know more"
- Always Remember:
- Transport layer protocols: TCP & UDP
- Application layer protocols: HTTP
- Network layer protocol: IP
- UDP:(User Datagram Protocol)
- It's a transport layer protocol
- Data may/may not be delivered
- Data may change on the way
- Data may not be in order
- UDP is a connectionless protocol: Which means no connection will be established between the two computers but it will still send the data
- UDP uses checksums: So you will know whether the data is corrupted or not
- but UDP will not do anything about it
- We use UDP because =>
- it's a lot faster
- Used in video calling apps
- DNS used UDP
- TCP:(Transmission Control Protocol)
- It's a transport layer protocol
- HTTP uses TCP
- Data is not lost
- Mechanism:
- The application layer sends lots of raw data --- TCP segments this data (divide in chunks, add headers etc)
- TCP maintains the order of data using sequence no.
- Features of TCP:
- Connection-oriented
- Full duplex
- Error control
- Congestion control
- 3-Way Handshake:(for TCP connection)
- This could also be seen as a way of how TCP connection is established
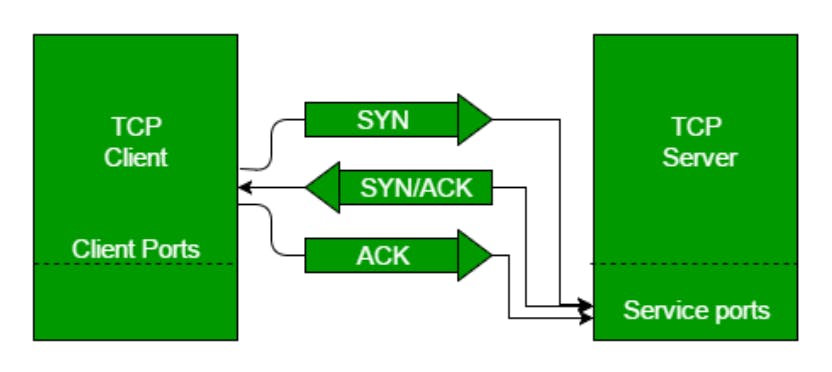
- The 3-Way Handshake process is the defined set of steps that takes place in the TCP for creating a secure and reliable communication link and also closing it.
- Machenism:
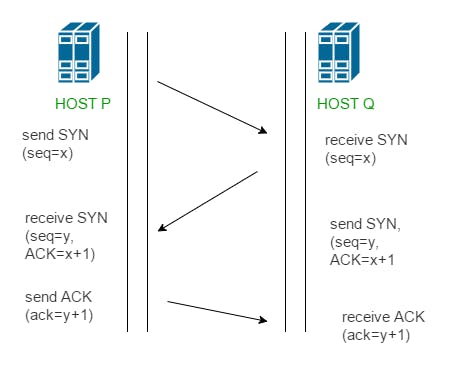
- Step 1 (SYN): In the first step, the client wants to establish a connection with a server, so it sends a segment with SYN(Synchronize Sequence Number) which informs the server that the client is likely to start communication and with what sequence number it starts segments with
- Step 2 (SYN + ACK): Server responds to the client request with SYN-ACK signal bits set. Acknowledgement(ACK) signifies the response of the segment it received and SYN signifies with what sequence number it is likely to start the segments with
- Step 3 (ACK): In the final part client acknowledges the response of the server and they both establish a reliable connection with which they will start the actual data transfer
NETWORK LAYER:
- Here we work with routers
- Every single router has its own network address
- Network address allows us to send the data packets to a router(lets say N1)
- This N1 is going to check its routing table
- Routing table consists of every destination address
- Control plane Control plane is used to build these routing tables
- Two types of routing:
- Static routing: where we add address manually
- Dynamic routing: This sort of evolves on its own ---> Algos like Dijkstra's etc are used
- Forwarding table is a subset of the routing table
- Routing table consists of every destination address
- IP:(Internet protocol)
- Its a network layer protocol
- Here we work with how the routing, control plane stuffs etc happen.
- IP address:
- IPV4 => These are 32 bit nos. with 4 words
- e.g.->
- IPV4 => These are 32 bit nos. with 4 words
- IP address:

- Good to know stuff:
- Earlier assigning of IP address used to happen on the basis of class(class A,B,C,D,E) but now it happens on the basis of regions
- IPV6 => These are 128 bits nos.
- It is 4 times larger than IPV4
- Cons:
- Not backward compatible
- ISPs would have to shift= Lot of hard work is needed
- Good to know stuff:
- Subnet Masking:
- Subnet masking means: It is going to mask the network part of the IP address and it will leave us to use the host part(device part)
- Middleboxes
- These are extra devices that also interact with IP packets
- Firewall:
- It filters out the IP packets based on various rules:
- Address
- Port nos.
- Flags
- Protocols
- Two types of firewalls:
- Stateless
- Statefull--> More efficient
- It filters out the IP packets based on various rules:
- Firewall:
- These are extra devices that also interact with IP packets
DATA-LINK LAYER:
- The datalink layer is responsible to send the packets(received from network layer) over a physical layer i.e. transport data between connected devices